So great I put it on my homepage.
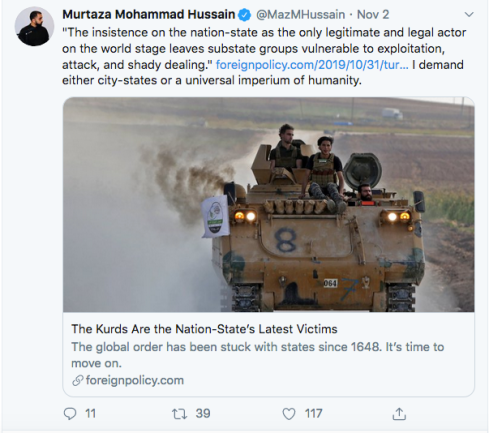
The Kurds Are the Nation-State’s Latest Victims
The global order has been stuck with states since 1648. It’s time to move on.
October 31, 2019, 3:47 PM
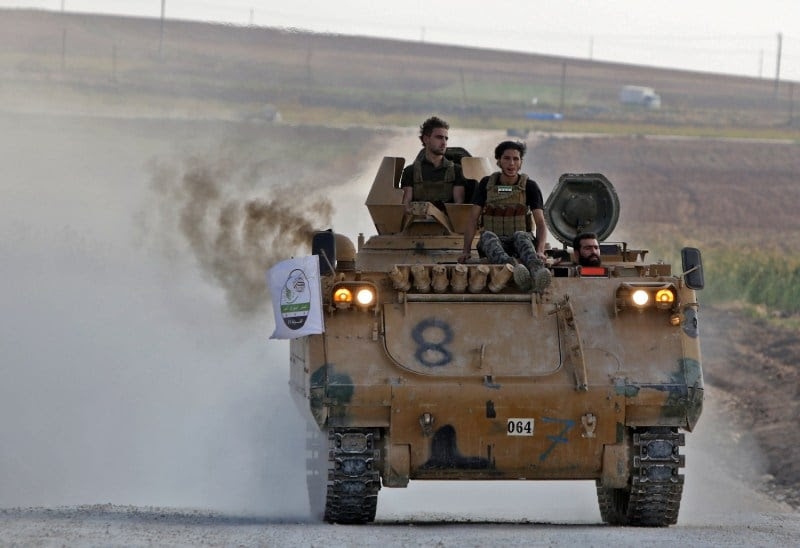

Turkey’s invasion of Kurdish-held areas of Syria is horrific and the decisions that led to it shameful. But it is also representative of a larger problem. The global system is built around sovereign states, and it shows. This is an enormous problem for groups that define themselves, or are defined by others, as distinct from the country within whose borders they happen to reside, and it’s also terrible as a framework for navigating the global politics of a rapidly changing world.
Sovereignty is usually traced back to the 1648 Treaty of Westphalia, which was pivotal in shifting conceptions of government toward a secular state with entire authority inside inviolable territorial borders. Designed as a diplomatic solution to catastrophic religious wars among feudal, monarchical territories, its tenets have persisted into the modern world largely due to the entrenched power of those states, jealously guarding their unfettered rule over their slice of geography. An arrangement of convenience between princes to end a religious war has become the be-all and end-all of the way the world is governed. Even as sovereigns in Europe fell, the idea of the nation came to the fore—with all its possibilities for excluding those who were not truly German or Italian or Polish. And even as European empires crumbled elsewhere in the world, they left behind a very particular view of nationhood.
Over the next several centuries, as the power of monarchy eroded and European countries needed something else to inspire loyalty among their citizens, the ideal of the nation-state—that the people within those arbitrary borders would feel some sort of collective identity—became popular. This led to more wars as European states expelled or converted anyone who didn’t fit their concept of nation: not French enough, not German enough, not Italian enough. They also spread this idea to their colonies, exporting successive waves of destructive conflicts.
Today, norms have shifted to a greater focus on individual rights, and power has eked out to nonstate players, but governments still harass, expel, and attempt to exterminate minority groups in the name of the nation-state ideal, and sovereignty still gives them carte blanche to do so.
The insistence on the nation-state as the only legitimate and legal actor on the world stage leaves substate groups vulnerable to exploitation, attack, and shady dealing.
The Kurds have been promised and denied so many times over the past century that it would be a wonder that they trusted anyone anymore if they had a choice. But the issue isn’t limited to the Kurds. In the news this week are Rohingya refugees stuck between two countries that don’t want them, Uighurs forced into detention camps, and Catalan protests for independence. History offers even more parallels, from the United States repeatedly breaking treaties with Native Americans to World War II, in which the United States was willing to go to war to protect the territorial integrity of France along with the people in it but was not willing to accept refugees fleeing the Holocaust. The nation-state system is designed to protect itself and its members, rather than people.
–
True, strong states screw over weaker states sometimes, too. But nonstate groups are at a particular disadvantage. Though they may hold de facto territory, they don’t hold it legally; they have no international rights to a military or to self-defense. They have no seat in international or supranational organizations, leaving them outside global decision-making and with no recourse in attempting to hold states accountable for their actions. Their leaders are not accorded head of state status, and they have no official diplomats. Since even the most generous autonomy statutes don’t confer the protections of statehood, separatist groups are often willing to risk high losses to win independence, fueling conflicts.
The global order provides more mechanisms for states to deal diplomatically with each other than with the people inside them. While interstate conflicts have fallen over the past 50 years, intrastate fighting has soared. These wars disrupt trade and world politics, weaken countries, and raise uncertainty in neighboring states. On the other hand, states have proved themselves adept at using substate actors to further their own interests within foreign countries while evading responsibility for it, from the United States arming the Contras in Nicaragua to Sudan and Chad supporting each other’s rebel movements.
The state-focused global order has shown itself poorly equipped to deal with these conflicts. States remain reluctant to break the collective agreement on the legitimacy of sovereignty. They are similarly reticent about adding more states to their exclusive club, in part because it might suggest to dissidents within their own area that renegotiation of borders is possible. Although a large number of states emerged from the Soviet Union in the 1990s, and there have been a few more recent exceptions such as Timor-Leste and South Sudan, it remains difficult to garner international recognition for a new state. That leaves mediators attempting to convince vulnerable groups to settle for something less, in the face of all evidence that a recognized state is their best chance for security and self-determination.
There have been some efforts to mitigate the effects of sovereignty. The responsibility to protect movement posits that states must protect their citizens and that if they fail to do so, others can step in to assist. It is intended as a way to justify and streamline the use of U.N.-sanctioned force in saving populations from genocide or other attacks perpetrated by the government they are subject to, but so far at least it has not proved successful as a way of overcoming the reluctance to breach sovereignty.
Substate groups are not the only example that the system is failing. Nonstate actors from terrorist groups to multinational corporations have increasing impacts on global politics, and traditional geopolitical theory does not do a great job of dealing with them. Even for bilateral issues, the nation-state is not always the most useful unit of analysis.
Take the numerous headlines and articles proclaiming that Russia interfered in the 2016 U.S. presidential election. To imagine this as a coherent national policy designed to attack the United States is not an accurate depiction of reality. Russia is not a democracy, and such interference is not aimed at, for example, winning territory from the United States. A more precise description would be that Russian elites attempted to tip the scales of U.S. leadership in order to win more modern spoils: unfettered soft power in their region, access to trade, and, notably, the ability to infringe on other countries’ sovereignty without consequences.
[my emphases throughout above]
*************************************************************************************
–
Comment: nikobakos@gmail.com
–

 An Armenian woman and her children who were refugees of the massacres and sought help from missionaries by walking far distances. Photo unknown provenance.
An Armenian woman and her children who were refugees of the massacres and sought help from missionaries by walking far distances. Photo unknown provenance. Armenian victims of the massacres being buried in a mass grave at Erzerum cemetery. Photo unknown provenance.
Armenian victims of the massacres being buried in a mass grave at Erzerum cemetery. Photo unknown provenance.